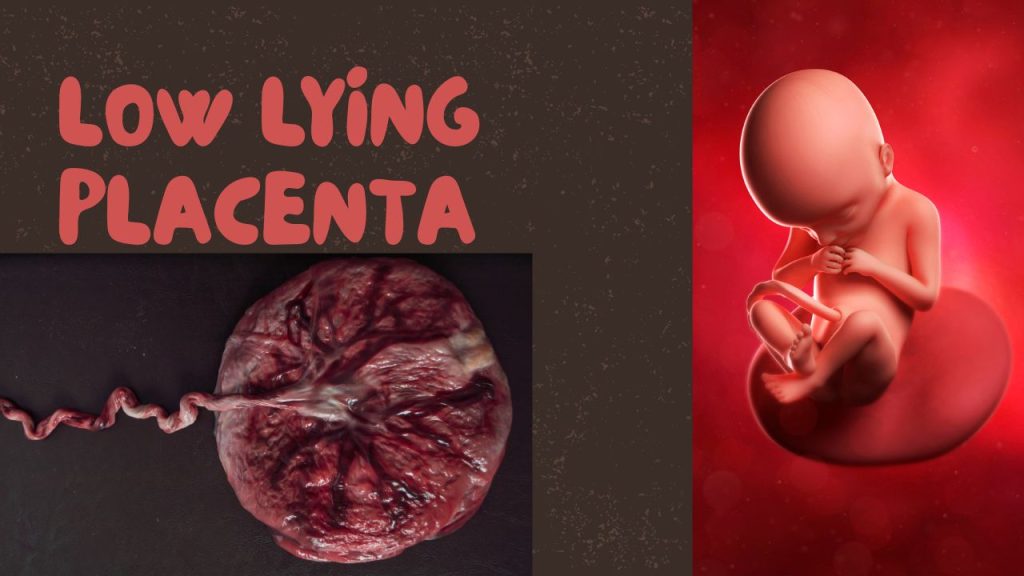
Learn about low lying placenta in pregnancy—causes, risks, ultrasound findings, safe exercises, diet tips, and treatment options.
Pregnancy comes with a lot of new terms and medical findings that can seem confusing and even scary. One such term is low lying placenta. If you’ve recently been told during an ultrasound that you have this condition, you may be worried about what it means for your pregnancy and your baby. Don’t worry — you’re not alone, and in most cases, it’s not as dangerous as it sounds. Let’s break it down in simple terms.
What is a low lying placenta?
An organ called the placenta develops throughout pregnancy to give your unborn child oxygen and nourishment. It is typically affixed to the upper part of the uterus. However, occasionally the placenta lies closer to the cervix and is positioned lower than usual. We refer to this as a low lying placenta.
Doctors usually detect it during a routine second-trimester ultrasound, often between 18 and 20 weeks. Many moms-to-be hear the term for the first time at this appointment.
The Risk of Low Legged Placenta in a Second Trimester Ultrasound
When an ultrasound report mentions a low lying placenta in the second trimester, it can be worrisome. But here’s some good news — most of the time, as your pregnancy progresses, your uterus grows and the placenta “lifts.” In fact, about 90% of cases resolve naturally by the third trimester.
Is a low lying placenta a problem at 13 weeks?
If you’re told at 13 weeks that you have a low lying placenta, it’s usually too early to worry. Your uterus is still small, and the placenta often looks low. As your uterus expands, the placenta will start to lift on its own. Doctors usually recommend waiting until a later ultrasound to see if it has moved.
Cervical Os MM Chart Low-Length Placenta Distance
Doctors often measure the distance between the placenta and the cervix, also known as the “cervical os.” They may mention the numbers in millimeters (mm) on your ultrasound report. This distance is important:
More than 20 mm away → Generally considered safe for a vaginal delivery.
Less than 20 mm away → Monitoring and sometimes a C-section may be needed.
A low lying placenta distance from the Cervical Os MM chart helps your doctor determine your delivery options.
What does posterior low lying placenta mean?
When your report says posterior low lying placenta, it means the placenta is attached to the back wall of the uterus but is still close to the cervix. Posterior just refers to the position — it’s not worse or better than anterior (front). What matters is the distance from the cervix.
Managing a low lying placenta with a previous C-section scar
Doctors pay extra attention if you have had a previous cesarean delivery. A low lying placenta with a C-section scar can sometimes increase the risk of placenta accreta (where the placenta is attached too deeply). In such cases, your doctor will monitor you more closely and may recommend a planned C-section.
Will a low lying placenta resolve by 32 weeks?
Many mothers ask: “Will a low lying placenta resolve by 32 weeks?” The answer is: Most often, yes. By the third trimester, most placentas move higher. If it doesn’t resolve by 32 weeks, your doctor will continue to monitor you. Some placentas stay low until delivery, and that’s when doctors make the final plan for the birth.
Does a low lying placenta cause a difference in the baby’s movement?
Another common concern is whether a low lying placenta affects the baby’s kicks. Does a low lying placenta cause a difference in the baby’s movement? Usually, no. The position of the placenta does not prevent your baby from moving. However, if the placenta is anterior (in front), it can hinder movement, making him feel sluggish. But a low lying placenta does not reduce your baby’s activity.
Diet restrictions for a low lying placenta pregnancy
Good news — there are usually no strict dietary restrictions for a low-lying placenta. You can eat a normal, balanced pregnancy diet. Some doctors may recommend avoiding foods that thin the blood (like too much papaya or pineapple), but in most cases, your food choices don’t affect the position of the placenta. The most important thing is to rest and avoid stress.
Symptoms of low lying placenta bleeding
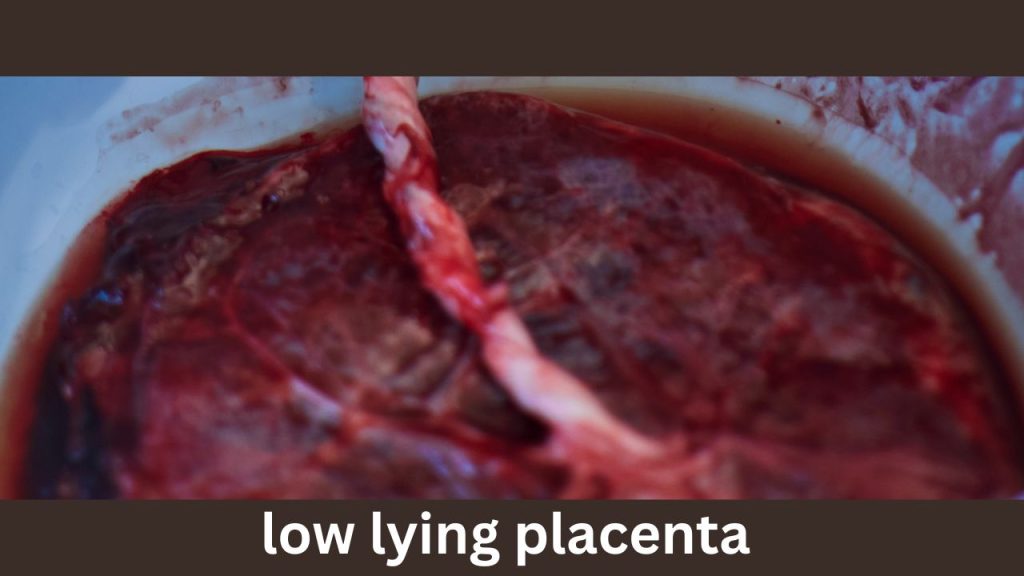
Many women wonder if there are non-bleeding symptoms of a low-lying placenta. In truth, most women don’t have any symptoms. The condition is often only detected on an ultrasound. However, if there is bleeding, especially in the third trimester, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention.
Safe exercises with a low lying placenta
You may also be wondering: What exercises are safe with a low-lying placenta? While doctors often recommend avoiding heavy lifting, jumping, or high-impact exercise, light activities are usually fine. Safe options include:
Gently walking
Yoga for pregnant women (with adjustments)
breathing and stretching techniques.
Before beginning or continuing an exercise routine while pregnant, always get your doctor’s approval.
Final thoughts
It may be disconcerting to know that you have a low-lying placenta, but in most cases, it resolves naturally and does not harm your baby. The key is to get regular checkups, follow your doctor’s advice, and avoid unnecessary stress. Remember, many mothers with this diagnosis have healthy pregnancies and births.